Hey there! As a supplier of 2 - Nitroaniline, I've had my fair share of experiences in its synthesis. Controlling the reaction conditions in the synthesis of 2 - Nitroaniline is super crucial, 'cause it can really affect the quality and yield of the final product. So, I'm gonna share some tips on how to do just that.
First off, let's talk about the starting materials. For the synthesis of 2 - Nitroaniline, we usually start with aniline. Aniline is a pretty reactive compound, but we need to handle it with care. It's important to use high - quality aniline, 'cause impurities can mess up the reaction. Make sure it's pure and free from any contaminants. You can get reliable aniline from good chemical suppliers.
Now, when it comes to nitration, which is a key step in making 2 - Nitroaniline, we need to control the nitrating agent and the reaction temperature. The most common nitrating agent is a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid. This mixture forms the nitronium ion ((NO_2^+)), which is the active species that reacts with aniline.
But here's the thing, if the reaction temperature is too high, we might get a lot of side products. For example, we could end up with more of the 4 - Nitroaniline or even dinitrated products. So, we need to keep the temperature low, usually around 0 - 5°C. You can use an ice bath to achieve this. It's like giving the reaction a nice, cool environment to work in.
The ratio of the reactants also matters a great deal. We need to carefully measure the amount of aniline, nitric acid, and sulfuric acid. Too much nitric acid can lead to over - nitration, while too little won't give us enough of the desired 2 - Nitroaniline. A typical ratio might be something like 1 mole of aniline to a specific amount of the nitrating mixture, but this can vary depending on the specific reaction setup.
Another factor to consider is the reaction time. We can't just let the reaction go on forever. Once the reaction is complete, we need to stop it. You can monitor the progress of the reaction using thin - layer chromatography (TLC). This is a handy technique that can show us if the starting material (aniline) has been consumed and if the 2 - Nitroaniline has been formed.
After the nitration step, we need to separate the 2 - Nitroaniline from the reaction mixture. This usually involves a series of steps like dilution, filtration, and recrystallization. Dilution helps to stop the reaction and make it easier to handle the mixture. Filtration removes any solid impurities, and recrystallization helps to purify the 2 - Nitroaniline. We can use solvents like ethanol or water for recrystallization. The choice of solvent depends on the solubility of 2 - Nitroaniline at different temperatures.
Let's also touch on safety. Working with concentrated acids is dangerous, so we need to wear proper protective equipment like gloves, goggles, and a lab coat. And make sure to work in a well - ventilated area to avoid inhaling any harmful fumes.
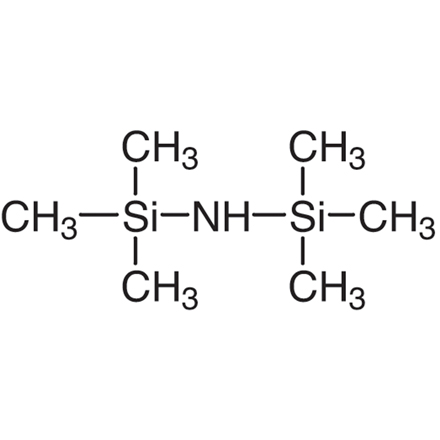
Now, I wanna mention a few related compounds and resources. If you're interested in some other chemical compounds, check out 25561 30 2. It might be useful in other chemical processes. Also, 1,1,1,3,3,3 - Hexamethyldisilazane Uses could give you some ideas about different applications in the chemical field. And for safety data on some related compounds, Safety Data Sheet PPD is a great resource.
In the synthesis process, we also need to pay attention to the pH of the reaction mixture. Sometimes, adjusting the pH can help in the separation and purification steps. For example, after the nitration reaction, we might need to neutralize the acidic mixture. We can use a base like sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide to do this. But again, we need to be careful not to add too much base, as it could cause other problems.
The purity of the final 2 - Nitroaniline is really important. We can use techniques like melting point determination and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to check the purity. A pure sample of 2 - Nitroaniline will have a specific melting point range. If the melting point is off, it could mean there are impurities in the sample.
When it comes to scaling up the synthesis, things get a bit more complicated. We need to make sure that all the reaction conditions are still under control. For example, the heat transfer might be different in a larger reaction vessel. We might need to use more sophisticated equipment to maintain the low temperature and proper mixing.
We also need to think about the storage of 2 - Nitroaniline. It should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from heat and light. And it should be kept in a properly labeled container to avoid any mix - ups.
If you're in the market for high - quality 2 - Nitroaniline, I'm here to help. As a supplier, I can offer you products that are synthesized under carefully controlled conditions. Whether you need a small amount for research purposes or a large quantity for industrial use, I've got you covered. Just reach out and we can start a conversation about your requirements.

In conclusion, controlling the reaction conditions in the synthesis of 2 - Nitroaniline is a multi - faceted process. We need to pay attention to the starting materials, reaction temperature, reactant ratios, reaction time, and purification steps. By doing so, we can ensure a high - quality product with a good yield. If you have any questions or want to discuss further about 2 - Nitroaniline synthesis or procurement, don't hesitate to get in touch.
References:
- Smith, J. Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. 3rd ed., Publisher, Year.
- Jones, A. Chemical Reaction Engineering. 2nd ed., Another Publisher, Another Year.



